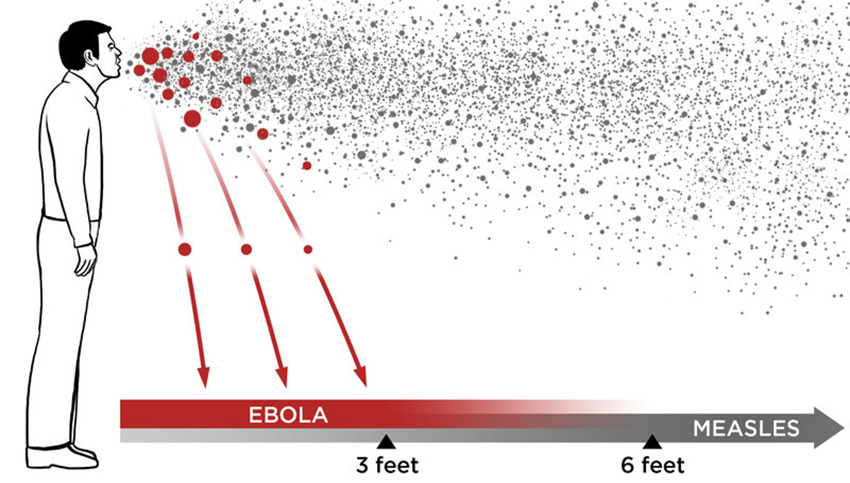
Airborne spread
The Corona Virus Can Be Airborne And Can Be Conditionally Spread Via Aerosol Transmission
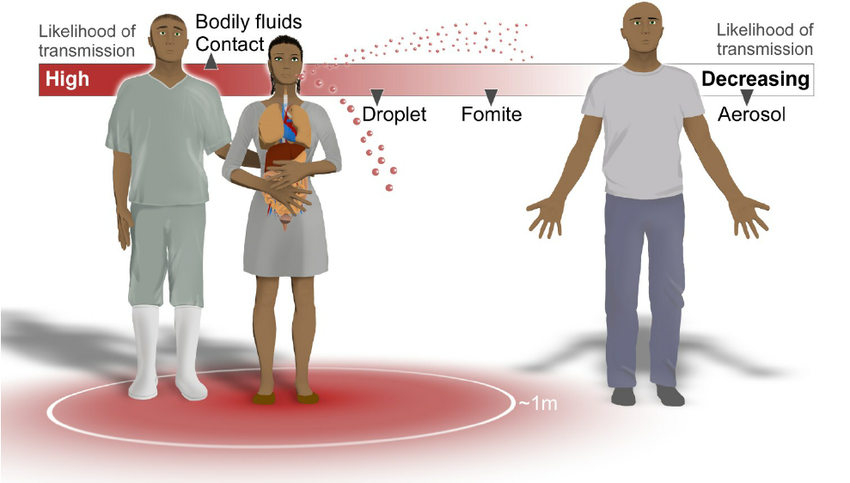
Source: Thailand Medical News Feb 20, 2020
How Contagious is Corona virus
The new coronavirus is a respiratory virus which spreads primarily through droplets generated when an infected person coughs or sneezes, or through droplets of saliva or discharge from the nose. To protect yourself, clean your hands frequently with an alcohol-based hand rub or wash them with soap and water.
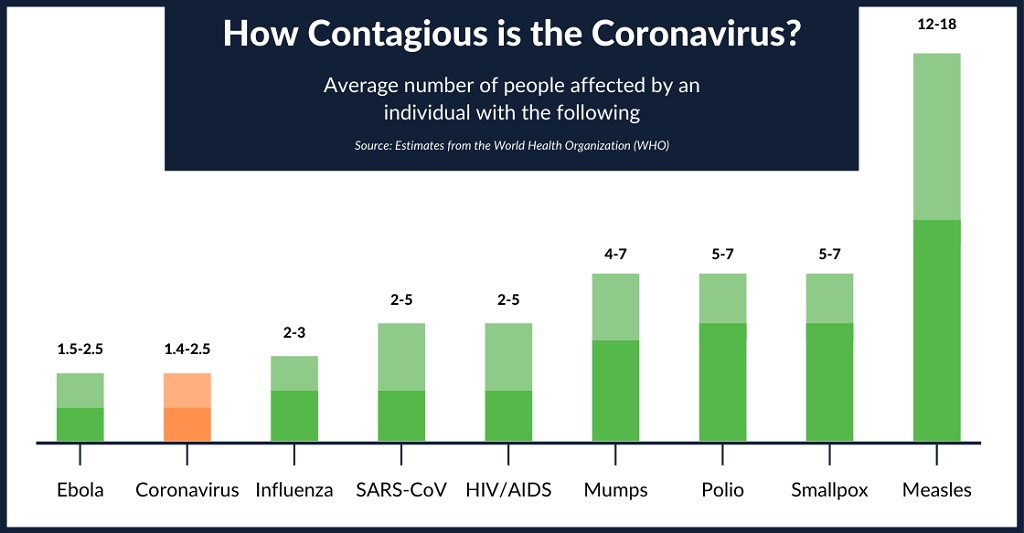
Source : Estimates from the World Health Organization(WHO)
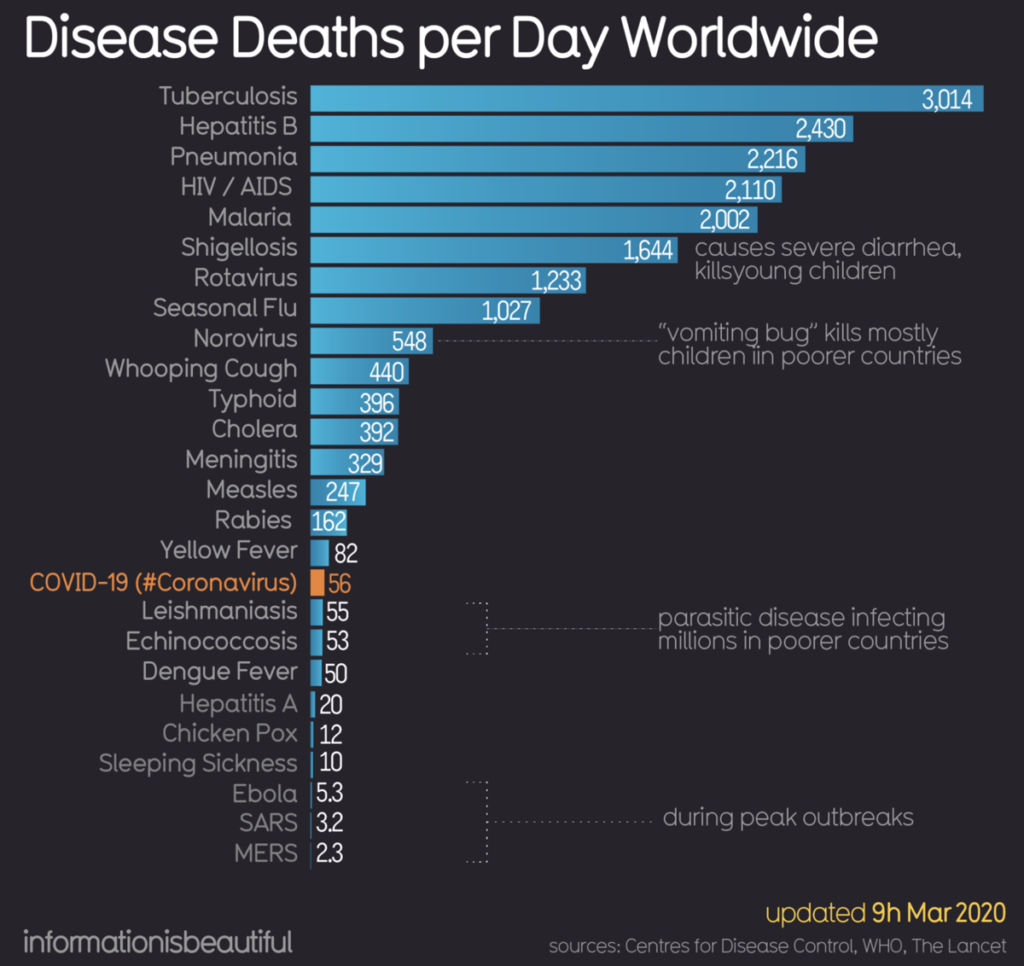
Context to other diseases
Comparison of Symptoms between cold, fever and COVID-19
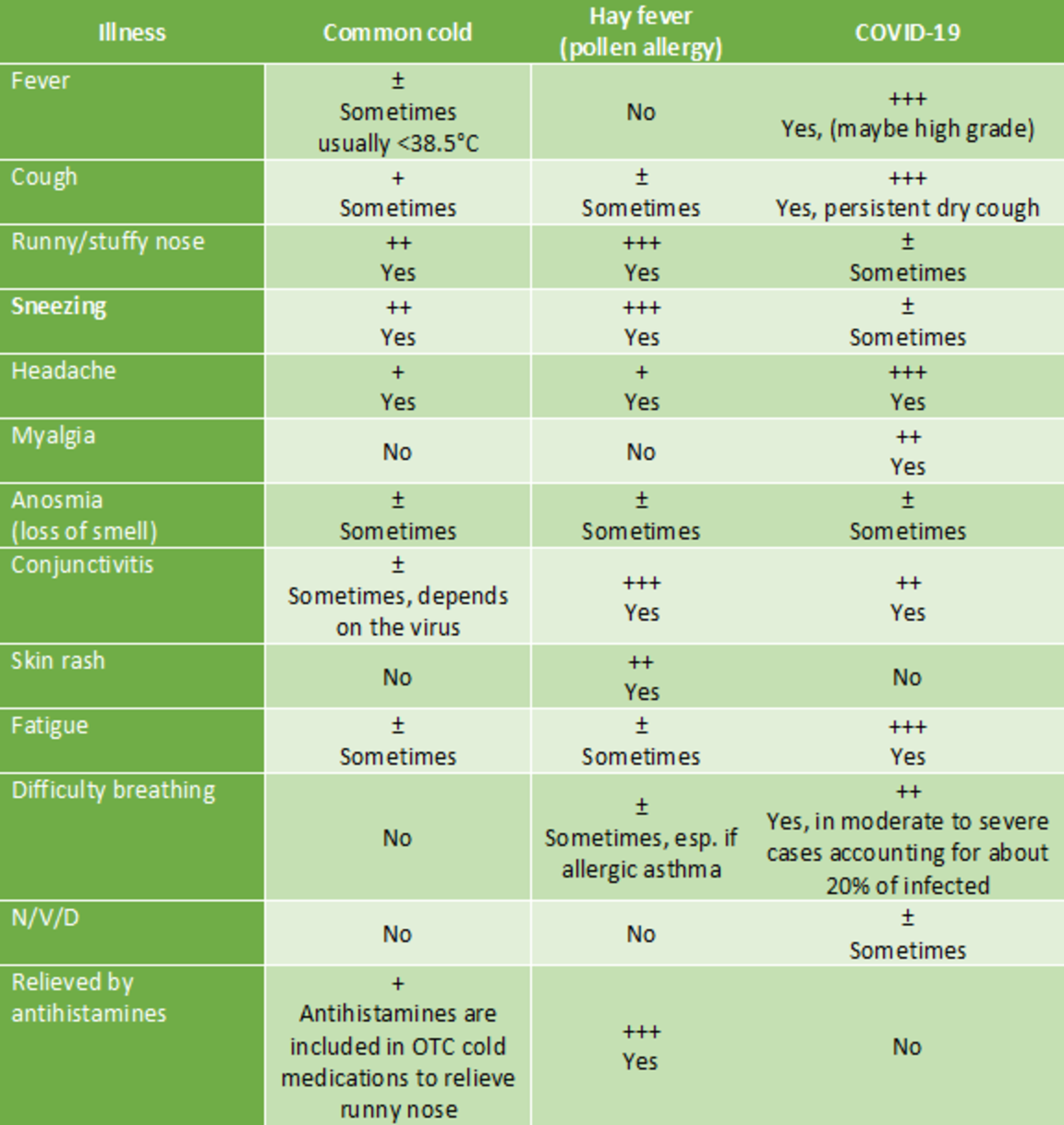
Source : "https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/covid-19/questions-answers/"
CORONAVIRUS-Symptoms
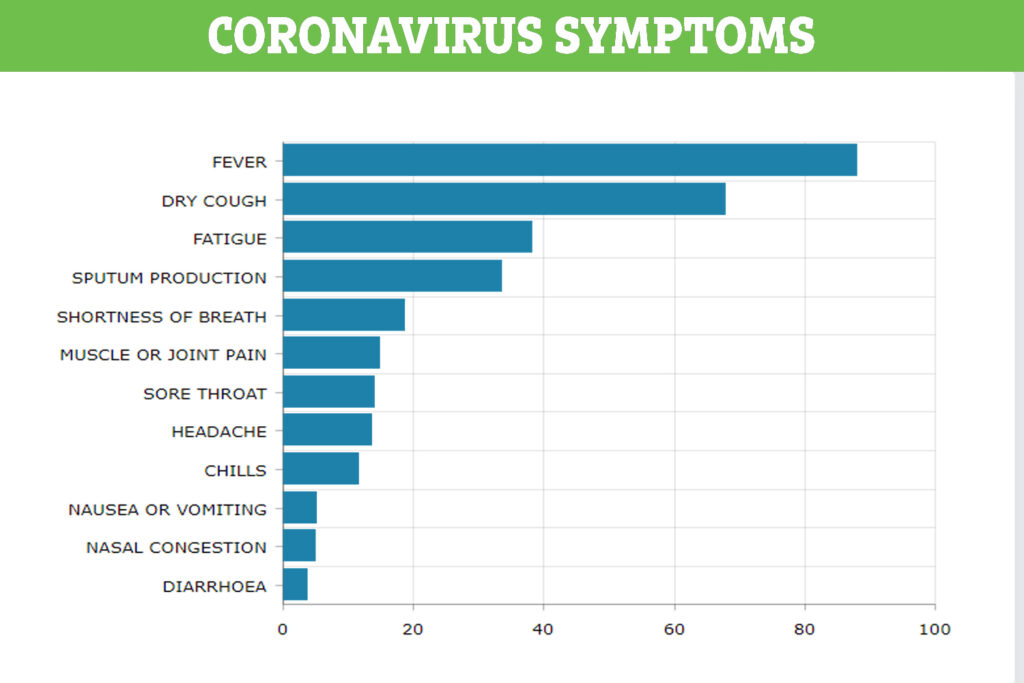
Source : "https://www.the-sun.com/news/609193/is-a-headache-a-symptom-of-coronavirus/"
Similar Viruses
| Name | Time period | Type / Pre-human host | Death toll |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antonine Plague | 165-180 | Believed to be either smallpox or measles | 5M |
| Japanese smallpox epidemic | 735-737 | Variola major virus | 1M |
| Plague of Justinian | 541-542 | Yersinia pestis bacteria / Rats, fleas | 30-50M |
| Black Death | 1347-1351 | Yersinia pestis bacteria / Rats, fleas | 200M |
| New World Smallpox Outbreak | 1520 – onwards | Variola major virus | 56M |
| Great Plague of London | 1665 | Yersinia pestis bacteria / Rats, fleas | 100,000 |
| Italian plague | 1629-1631 | Yersinia pestis bacteria / Rats, fleas | 1M |
| Cholera Pandemics 1-6 | 1817-1923 | V. cholerae bacteria | 1M+ |
| Third Plague | 1885 | Yersinia pestis bacteria / Rats, fleas | 12M (China and India) |
| Yellow Fever | Late 1800s | Virus / Mosquitoes | 100,000-150,000 (U.S.) |
| Russian Flu | 1889-1890 | Believed to be H2N2 (avian origin) | 1M |
| Spanish Flu | 1918-1919 | H1N1 virus / Pigs | 40-50M |
| Asian Flu | 1957-1958 | H2N2 virus | 1.1M |
| Hong Kong Flu | 1968-1970 | H3N2 virus | 1M |
| HIV/AIDS | 1981-present | Virus / Chimpanzees | 25-35M |
| Swine Flu | 2009-2010 | H1N1 virus / Pigs | 200,000 |
| SARS | 2002-2003 | Coronavirus / Bats, Civets | 770 |
| Ebola | 2014-2016 | Ebolavirus / Wild animals | 11,000 |
| MERS | 2015-Present | Coronavirus / Bats, camels | 850 |
| COVID-19 | 2019-Present | Coronavirus – Unknown (possibly pangolins) | 70,600 (Johns Hopkins University estimate as of 9am PT, April 6) |
Note: Many of the death toll numbers listed above are best estimates based on available research. Some, such as the Plague of Justinian and Swine Flu, are subject to debate based on new evidence.
Source : "https://www.visualcapitalist.com/history-of-pandemics-deadliest/"