Study Shows Beneficial Effects of Vitamin D in COVID-19
November 20, 2020
Long Covid
December 25, 2020Study Shows Mindfulness Training Reduces Severity of Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome in Women
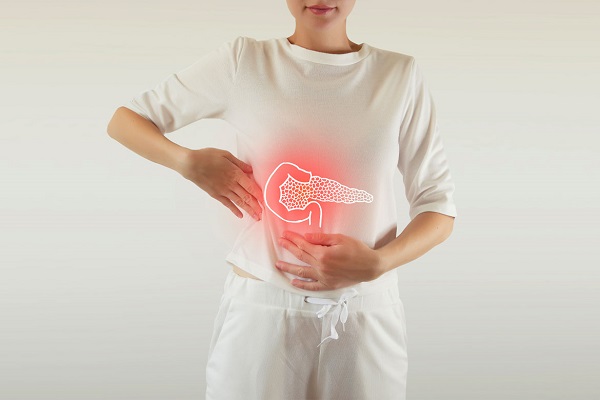
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common medical condition. It is a functional bowel (gut) disorder, and it is a chronic condition, other names given to it are nervous colon, spastic bowel etc.
It is more common among women than in men and about 10% of American adults suffers through it. Moreover, People suffering through anxiety, depression and other mental issues and people with a positive family history are more prone to develop IBS.
Signs and symptoms of IBS may include, abdominal pain or cramping, bloating, gas, diarrhea, constipation, while some may experience constipation alternating with episodes of diarrhea, difficulty in passing stools, a feeling of incomplete evacuation, sudden urgent need to use toilet, mucous in stools etc. These symptoms are often accompanied by other symptoms such as urinary symptoms, depression, anxiety, back pain, sleep disturbances, head ache etc.
Although the nature of the disease is benign, it can severely affect an individual’s quality of life. Social activities away from home can become difficult due to abdominal discomfort, pain or inaccessibility to wash room.
The exact or precise cause of IBS is not known but according to researchers some factors that may play a role, such as;
*Poorly coordinated signals between brain and intestines can cause colon (large intestine or gut) to become hypersensitive and over reactive to mild stimulation, such as passage of solid, gas and fluids through intestine. The muscles in the walls of the intestine contract as they move food through the digestive tract. Stronger contractions in the walls of intestine which last longer than normal can cause diarrhea as well as gas and bloating, whereas weaker contractions can slow down food passage and can lead to constipation.
*IBS can also occur after acute gastroenteritis or digestive tract infection caused by bacteria or virus.
*IBS might be associated with bacterial overgrowth in the intestines (gut).
*Physical and emotional stress also plays a key role; people exposed to stressful events especially during childhood tend to develop symptoms of IBS in later life.
*Moreover, IBS patients may experience severity in their symptoms when they consume certain food or beverages such as wheat, milk, dairy products, citrus fruit, beans and carbonated drinks etc. Unhealthy eating patterns and antibiotic use can also affect IBS symptoms.
Since there is no physical abnormality present in IBS, diagnosis mainly depends upon symptoms and thus it has no specific diagnostic test.
Life style modifications, stress management, and avoiding food which could aggravate symptoms of IBS can play a role in controlling symptoms of IBS. More severe symptoms can be treated and managed with medications and counselling.
IBS results in significant disability, quality of life impairment and health care burden. Conventional medical care for IBS has primarily focused on diet and life style management, behavioral treatments, pharmacological agents (medications) particularly antispasmodics (It is a pharmaceutical drug or other agent that suppresses muscle spasms).
A substantial proportion of patients with IBS do not attain adequate relief through conventional medical approaches. Pharmacological therapies may temporarily relieve symptoms; they are often costly and may result in negative side effects.
This has led to efforts to find other methods to improve clinical outcomes for IBS patients.
Recently, scientists have conducted studies with an objective to determine and explore the feasibility and efficacy of a group program of mindfulness training; a cognitive-behavioral technique, for women with IBS.
[Cognitive-behavioral technique or therapy is psycho-social intervention that aims to improve mental health and helps people learn how to identify and change destructive or disturbing thought patterns that have a negative influence on behavior and emotions. It is focused on using a wide range of strategies to help people overcome these thoughts which may include relaxation techniques, mental distractions, journaling etc.]
Experts suggest that psychological interventions such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and hypnosis have proven among the most successful treatments for IBS. Psychological treatments are logical approach to management of the bowel symptoms of IBS as brain- gut interactions are recognized to have a prominent role in modulating gut functions.
Through mindfulness practice, one learns to evoke a non-evaluative state of present moment awareness. The basic technique of mindfulness involves the intentional self-regulation of attention to present moment experience using breath or other object as focal point and letting go of thoughts, feelings and story lines that may enhance pain, evoke stress, and induce catastrophizing about negative events.
Researchers theorized that mindfulness may have beneficial effects on experiences and symptoms of IBS patients.
To conduct the studies 75 female IBS patients were randomly assigned to eight weekly and one-half day intensive sessions of either mindfulness group (MG) training or a support group (SG).
[Support groups are defined as meeting of people with similar experiences. A support group provides an opportunity for people to share personal experiences and feelings, coping strategies or first-hand information about disease or treatments.]
Results of the studies have shown that women in the MG showed greater reductions in IBS symptoms severity immediately after training and at 3 months follow-up relative to SG.
Moreover, changes in the quality of life, psychological distress and visceral anxiety (It is a form of anxiety experienced by some subjects with gastrointestinal problems) were not significantly different between the groups immediately after treatment, but significantly greater improvements were noted in MG as compared to the SG at 3- months’ follow-up.
Through the studies researchers concluded that mindfulness training has a substantial therapeutic effect on bowel symptoms severity, improves health related quality of life and also reduces distress. Furthermore, the beneficial effects of the mindfulness training persist for at least 3 months after group training.
REFERENCE:
Mindfulness Training Reduces the Severity of Irritable Bowel Syndrome in Women: Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial